Linked list
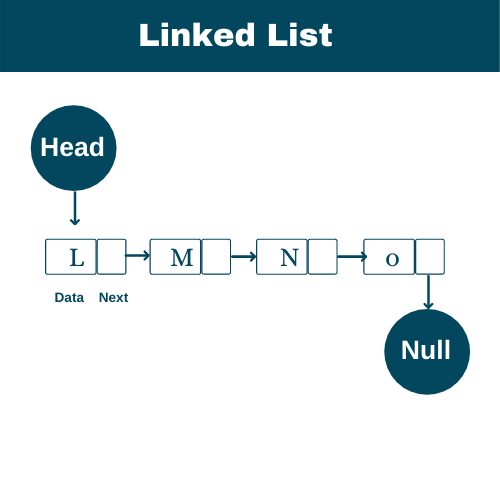
What is a linked list?
- Are container where data is stored in nodes
- The nodes consist single data item and pointer/reference to the next node
What is a node?
- The node is nothing but a link in the linked list
- The node contains two things
- It contains a value
- Its contain reference to the next list
Types of linked list
- Singly-linked list
- Doubly linked list
Singly-linked list
- Is a linked list that provides forward iteration from the start to the end of the list
- The iteration starts from the first node and ends at the last node
Doubly linked list
- Is a linked list that provides forward iteration from the start to the end of the list and reverses iteration from end to start
- Traversing from the current node to the next and previous node is possible
Singly vs Doubly linked list
- Singly-linked list requires lesser memory compared doubly
- Singly-linked list cant be iterated in reverse while doubly linked can be
- Deleting the previous node in doubly linked doesn’t require traversing
Write a code
Let’s write a linked list in javascript
// Linked in Javascript
class LinkedList {
constructor(data) {
this.head = {
data: data,
next: null
};
this.tail = this.head;
this.length = 1;
}
addData(data) {
const newNode = {
data: data,
next: null
}
this.tail.next = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
this.length++;
return this;
}
insert(index, data) {
if (index >= this.length) {
return this.addData(data);
}
const newNode = {
data: data,
next: null
}
const leader = this.traverseToIndex(index - 1);
const holdingPointer = leader.next;
leader.next = newNode;
newNode.next = holdingPointer;
this.length++;
return Promise.resolve(true);
}
traverseToIndex(index) {
let counter = 0;
let currentNode = this.head;
while (counter !== index) {
currentNode = currentNode.next;
counter++;
}
return currentNode;
}
remove(index) {
let traversingItem = index - 1;
if (index === 0) {
traversingItem = 0;
}
const leader = this.traverseToIndex(traversingItem);
const removeNode = index === 0 ? null : leader.next;
leader.next = index === 0 ? null : removeNode.next;
this.length--;
return Promise.resolve(true);
}
}
let linkedListInstance = new LinkedList(1);
linkedListInstance.addData(2);
linkedListInstance.addData(3);
linkedListInstance.insert(2, 99);
linkedListInstance.insert(5, 88);
console.log(linkedListInstance);
// LinkedList {
// head: { data: 1, next: { data: 2, next: [Object] } },
// tail: { data: 88, next: null },
// length: 4
// }